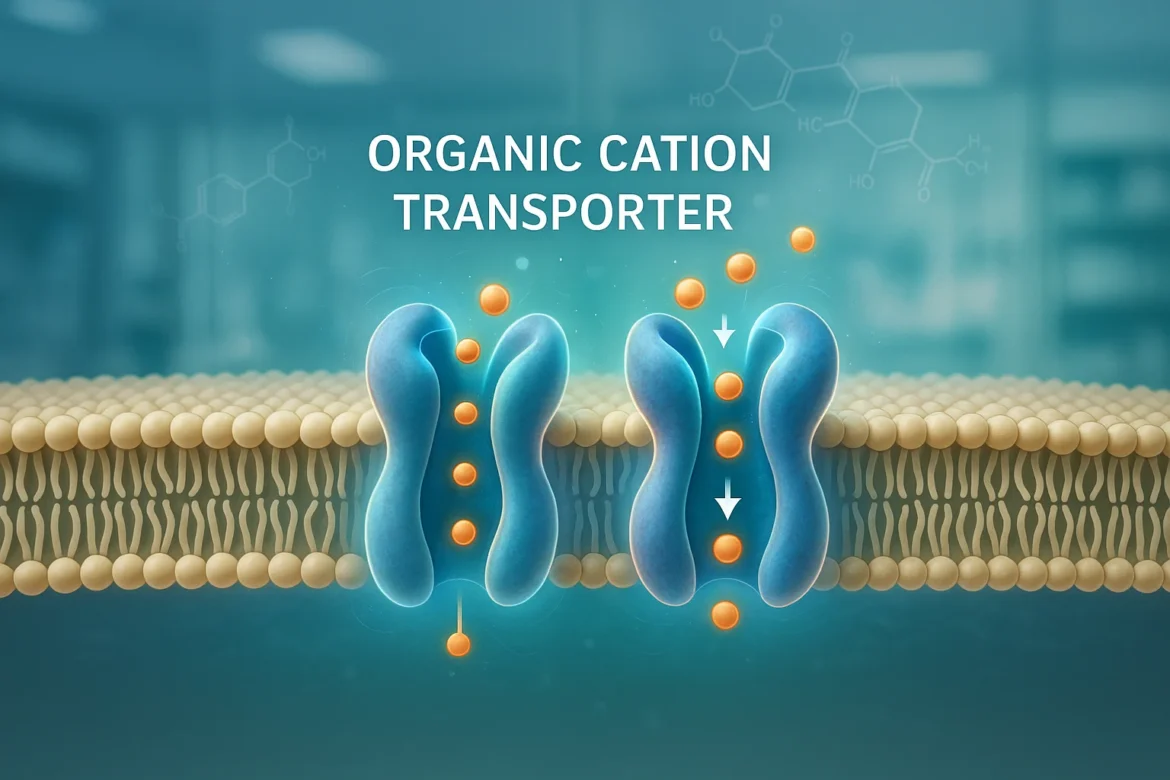
Organic Cation Transporter, commonly abbreviated as OCTs, are specialized proteins found in cell membranes. They play a vital role in the transport of positively charged organic molecules—known as cations—across cell membranes. These molecules can include neurotransmitters, drugs, toxins, and metabolic waste.
Unlike passive diffusion, OCTs enable active transport, meaning they can carry substances against concentration gradients, often powered by membrane potentials. They are especially critical in organs such as the liver, kidneys, and brain, where they help regulate drug excretion, detoxification, and absorption.
🧠 The Biological Importance of OCTs
In the central nervous system, OCTs help maintain neurotransmitter balance by transporting molecules like dopamine and serotonin. This function makes them important targets for psychiatric and neurological drug development.
In the kidneys, OCTs play a crucial role in filtering out harmful substances and returning necessary compounds to the bloodstream. The liver also relies on them to process and eliminate metabolic waste through bile secretion.
💊 OCTs and Drug Interactions
One of the most intriguing aspects of organic cation transporter is their role in pharmacokinetics—how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Many commonly used medications, such as metformin (used for Type 2 diabetes), rely on OCTs to reach their target sites or to be eliminated from the body.
When two drugs compete for the same transporter, it may result in drug-drug interactions. This is why understanding OCT activity is critical during drug development and clinical trials.
🧪 Types of Organic Cation Transporter
There are three main human OCTs categorized under the SLC22A gene family:
- OCT1 (SLC22A1) – Primarily found in the liver
- OCT2 (SLC22A2) – Dominant in the kidneys
- OCT3 (SLC22A3) – Widely distributed across tissues including the brain, heart, and placenta
Each of these has different substrate specificities and tissue localization, which makes them uniquely important in pharmacological and physiological contexts.
⚠️ Clinical Relevance of OCT Dysfunction
Disruption or genetic variation in OCT genes can significantly impact a person’s ability to metabolize drugs or toxins. For example, reduced OCT1 function may lower the effectiveness of metformin, leading to poor glycemic control in diabetic patients.
Additionally, cancer therapies are being tailored to exploit OCTs for targeted drug delivery, enhancing treatment efficacy while reducing side effects.
🧬 OCTs in Personalized Medicine
With the rise of personalized medicine, OCT genotyping is becoming increasingly relevant. Patients may carry genetic variants that alter transporter efficiency, which can be used to customize drug type or dosage. Pharmacogenomics—tailoring medicine based on genetic makeup—relies heavily on understanding these transport proteins.
🔍 Research and Future Directions
Current research on organic cation transporters is focused on their potential in improving drug delivery and reducing side effects. Nanoparticle-based drug systems are being developed to utilize OCT pathways, especially in targeting tumor cells or crossing the blood-brain barrier.
Furthermore, OCTs are being investigated for their role in antibiotic resistance, as many bacterial pathogens use similar transport systems.
READ MORE…
Emergency Moving Services You Can Trust
Best Same-Day Movers in Dallas